
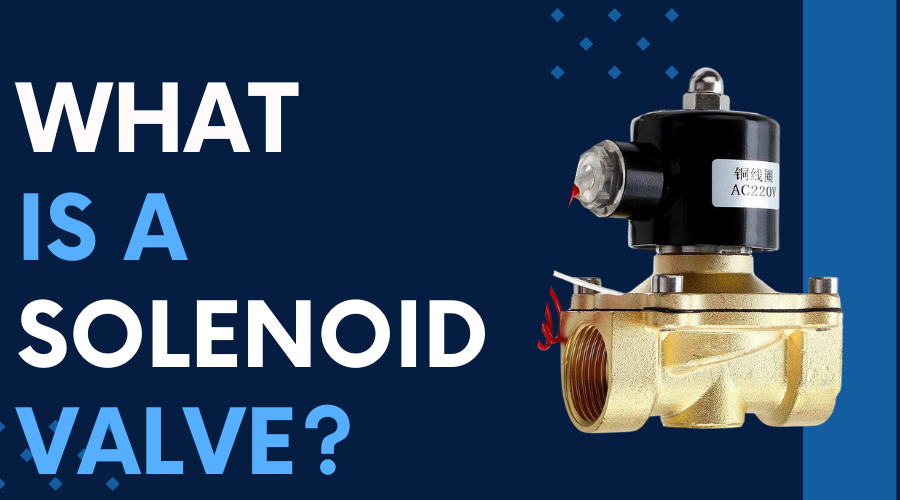
In the labyrinth of industrial machinery, one often encounters the term "solenoid valve" buzzing around like a diligent worker bee. But what exactly is a solenoid valve, and how does it play a pivotal role in the smooth operation of various mechanical systems? Let's embark on a journey to demystify the inner workings of these ingenious devices.
Solenoid valves, akin to silent guardians within the intricate machinery of our world, are electromechanical devices that control the flow of fluids. They operate by using electromagnetic forces to actuate a plunger, which, in turn, regulates the opening and closing of the valve.
Now that we've scratched the surface let's delve into the captivating science behind what makes a solenoid valve work. Picture this: a small but mighty coil of wire, often wound around a core, forming the heart of the solenoid. As an electric current courses through the loop, it creates a magnetic field, converting the solenoid into a magnet.
To truly grasp the marvel of solenoid valves, it's imperative to dissect their anatomy, akin to unraveling the intricate layers of a mechanical onion.
1. Wire Wonders: The coil, usually made of copper wire, exhibits a mesmerizing dance when subjected to electrical current. This dance is what propels the solenoid into action.
2. Core Considerations: Coiled around a core, often composed of ferrous materials like iron, the solenoid's core enhances the magnetic field, amplifying its strength and efficiency.
1. Material Matters: The plunger, a pivotal component, is crafted from materials with high magnetic permeability, such as iron or steel. This ensures a seamless response to the magnetic forces generated by the coil.
2. Return Spring Resilience: To maintain equilibrium, a return spring complements the plunger, ensuring it reverts to its original position once the magnetic forces cease, allowing for a cyclic, controlled motion.
Now, let's delve deeper into the mesmerizing dance of fluids orchestrated by solenoid valves.
1. Liquid Luminary: In applications involving liquids, solenoid valves effortlessly control the flow, whether managing coolant circulation in industrial machinery or facilitating the precise delivery of medication in healthcare settings.
2. Gaseous Gatekeepers: When dealing with gases, solenoid valves act as vigilant gatekeepers, allowing or restricting the flow with unparalleled precision. This is particularly crucial in industries reliant on gas processes, such as the petrochemical sector.
3. Beyond the Basics: Solenoid valves, with their adaptability, can even handle more exotic fluids, showcasing their versatility in industries dealing with specialized substances.
Close your eyes and imagine the tactile sensations, the subtle vibrations, as a solenoid valve springs into action.
1. Subtle Vibrations: When a solenoid valve activates, there's a tactile symphony—a slight vibration that resonates through the system, almost like the heartbeat of a well-oiled machine.
2. Precision Palpability: The precision with which solenoid valves operate is not just a visual spectacle; it's a tactile experience. Picture the delicacy of a surgeon's hand translated into industrial machinery.
While the electromagnetic dance is unseen, its effects manifest in a system's visible and impactful changes.
1. Invisible Forces, Visible Impact: Although the magnetic forces within a solenoid valve are hidden, their impact is visually apparent as valves open or close with the precision of a choreographed dance.
2. Dynamic Displays: In high-tech applications, visual indicators complement solenoid valves, providing real-time feedback on the valve's status. This optical element adds another layer of sophistication to the already intricate system.
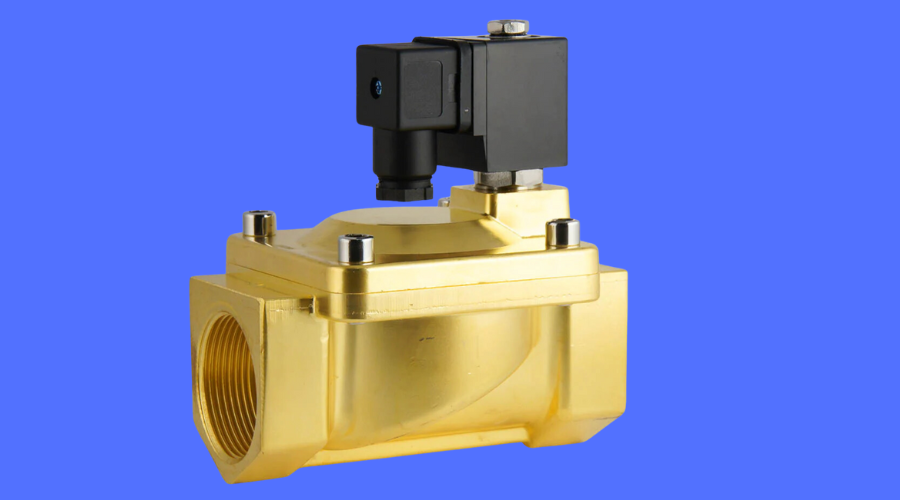

Solenoid valves, the unsung heroes of industrial automation, are at the heart of numerous applications, seamlessly orchestrating the symphony of mechanical processes.
In municipal water supply systems, solenoid valves regulate the flow, ensuring a controlled and efficient water distribution.
Precision is paramount in the medical field. Solenoid valves, with their quick response and accuracy, are pivotal in controlling fluid flow in medical equipment.
In gas-powered appliances, solenoid valves act as gatekeepers, allowing or disallowing the gas flow, ensuring safety and efficiency.
From controlling fuel injection systems to managing air intake, solenoid valves are the maestros behind the scenes in modern automobiles.
In manufacturing plants, solenoid valves choreograph the dance of fluids, enabling precise control in various processes, from production lines to chemical reactors.
Q1: Can solenoid valves be used for both liquids and gases?
Absolutely! Solenoid valves are versatile and can be adapted for liquids and gases, showcasing their flexibility across various industries.
Q2: How fast do solenoid valves respond to electrical signals?
Solenoid valves are renowned for their rapid response times, often opening or closing within milliseconds. This quick action is crucial in applications where precision is paramount.
Q3: Are solenoid valves energy-efficient?
Yes, indeed. Solenoid valves are known for their energy efficiency, as they only consume power when the state of the valve is actively changed. This makes them not only efficient but also cost-effective in the long run.
Q4: Can solenoid valves be used in harsh environments?
Many solenoid valves are designed to withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures and corrosive atmospheres. However, choosing the right type of valve for specific environmental challenges is essential.
As we conclude our exploration into the world of solenoid valves, it becomes evident that these unassuming devices are the unsung heroes of modern engineering. From regulating water flow in our cities to fine-tuning the performance of cutting-edge medical equipment, solenoid valves silently but powerfully shape the landscape of our technological era.
So, the next time you turn on your faucet or marvel at the precision of medical devices, take a moment to appreciate the intricate dance of electromagnetic forces within the heart of a solenoid valve. These unassuming devices might be the key players in the symphony of progress, orchestrating a harmonious blend of efficiency and control in our ever-evolving world.
Pneumatic angle sea valves are an important component that is vital for the functionality of any fluid control system like HVAC, water supply, or petroleum. Such valves perform the important function of regulating flow and transferring fluids under challenging conditions by the seamless managing of flow rate and pressure drop in a system keeping it working efficiently and preserving the condition of the system. In this blog we will engage in a detailed explanation of the working principle behind pneumatic angle seat valves, the factors that affect their performance and important tips to enhance their operational efficiency. Understanding Pneumatic Angle Seat Valves Any efficient fluid or gas pipeline system needs to maintain flow in the system, and the pneumatic angle seat valves are specialized flow control devices that regulate fluid flow in the system. Their operating mechanism consists of a pneumatic actuator that lifts the valve seat at a specific angle to ensure a smooth flow of fluid without any resistance. Angle seat valves are adaptable and can be used in all kinds of supply systems, whether air, water or any other fluid. Their adaptability makes them really useful in multiple industrial sectors. Types of Pneumatic Angle Seat Valves Single Acting Valves: feature a spring return mechanism which opens or closes when pneumatic pressure is exerted. Double Acting Valves: These valves require pneumatic pressure for both closing and opening. Key Components Actuator: delivers pneumatic power for valve operation Seat: provide an adequate seal for leakage resistance Piston/Diaphragm: drives movement within the actuator. The Role of Flow Rate and Pressure Drop in Valve Performance Flow rate in pneumatic valves The flow rate is basically the fluid volume that passes through the valve within a fixed time period. A constant and stable flow rate must be maintained for system efficiency and for, minimizing wear resistance and keeping up with the operational demand. Pressure Drop Explanation Once the fuid passes through the valve a pressure drop occurs always. If the pressure drop is a lot it is a symptom of system inefficiency as it signifies that energy is being wasted there is excessive load on the fluid system. Link Between Flow Rate and Pressure Drop There is a direct relationship between the flow rate and pressure drop. The higher the flow rate, the greater will be the pressure drop. But with a more efficient valve design and a secure system setup the negative impact of the pressure drop can be erased. A subtle balance needs to be preserved between multiple factors for maintaining a constant performance while reducing cost. Factors Affecting Flow Rate and Pressure Drop Valve Size and Design Larger valves are capable of maintaining a higher flow rate with less pressure drop. Design also helps in restricting pressure drops as they reduce turbulence and resistance. Fluid Viscosity and Types A fluid with a thicker consistency creates a higher resistance. This makes the pressure level fall higher. To avoid this it is better to study the fluid charachteristics and only then select the valve. System Configuration There are a number of system parameters that need to be taken into consideration to maintain an adequate flow. These consist of piping length, diameter, and layout configuration of the system. Layouts having sharp bends, narrow pipes or really long length increase the pressure drop. Environmental Factors Environmental conditions also have an affect on flow behavior. Temperature and altitude can interfere with fluid flow and this means that customized valves should be fitted that can handle the environmental changes. How to Manage Flow Rate in Pneumatic Angle Seat Valves Selecting the Right Valve for Your System System flow requirements vary from one fluid system to another. To make the correct choice of valves that best match the system consider features like type of fluid, operating pressure and the target flow rate. Proper Sizing Ensuring that the valve has an appropriate size is crucial for an efficient system performance. Too small valves can hinder the flow while too large valves can make the pipeline system inefficient. Adjustable Valves These kind of valves come fitted with features that allow multiple options for regulating flow and the flow can be varied according to changing demands. Flow Control Accessories There is an array of accessories that can be utilized to control the flow such as flow regulators and throttling devices. Such accessories can fine tune the system performance without putting load on the system. Managing Pressure Drop in Pneumatic Angle Seat Valves Minimizing Pressure Drop The best way to accomplish this is to keep the system design well-planned. Make use of streamlined pipe configuration and as much as possible avoid unnecessary bends. This will keep pressure drop on the safe size. Valve Configuration and Maintenance Maintenance is necessary for unobstructed fluid flow as it keeps the pipeline clean. Moreover rust can build up on the components interfering with flow and increasing resistance. With regular maintenance checks and cleaning will ensure uninterrupted fluid flow that keeps pressure fluctuations in check. Pipe Layout Should Be Adequate A well-designed pipe layout is crucial for reducing pressure losses. This can be done by utilizing wide pipes and using a uniform diameter size all over the pipeline system. Choose the Correct Valve Type for Pressure Control Fitting a system with specialized valves that are designed according to specific internal geometric design can ensure that pressure drop is not significant. Troubleshooting Flow Rate and Pressure Drop Issues Diagnosing Common Problems Reduced system efficiency, or fluid leakage is a sign of flow and pressure problems. These issues are best identified through routine monitoring. Solution Strategies Worn or damaged valves need to be replaced. The piping layout can be modified to improve flow characteristics. Air supply inconsistencies should be addressed to optimize the performance of the actuators. Improving System Efficiency Utilizing High-performance valves or advanced flow monitoring tools can have a great impact improving the overall efficiency of the system. Best Practices for Peak Flow Rate and Pressure Drop Routine Maintenance Schedule regular inspections to clean and replace worn parts. This will keep the system operating at its peak consistently. Monitoring Systems Fitting flow meters and pressure sensors for real-time insights will keep you updated about the system performance and it will be easier to take proactive adjustments in case of a problem. Training for Operators Give operators proper training on valve handling and system management to reduce operational errors and improve longevity. Using Quality Valves High-quality pneumatic angle seat valves are investments that ensure reliability and reduce the possibilities of problems arising while improving performance. Conclusion The flow rate and pressure drop in pneumatic angle seat valves should be controlled for proper maintenance of the system's efficiency and reliability. How these factors interact and choosing the appropriate components with best practices will optimize performance and save on costs. The keys to success are proactive maintenance and quality valve investment. FAQs 1. How do I know if my pneumatic angle seat valve is experiencing a pressure drop? You might notice a decrease in flow rate, inconsistent valve operation, or a drop in system pressure. 2. Can the flow rate be adjusted without replacing the valve? Yes, the flow rate can be adjusted by changing the valve's actuation method or by using flow control accessories. 3.What are the typical reasons for high pressure drop in pneumatic systems? Examples include; leakage, blocked filters, small pipes, and condensed water in the refrigeration system. 4. What makes valve sizing as a critical factor for controlling the flow rate and pressure drop? Valve sizing involves correct selection of valve sizes through appropriate means so that the flow may be adequately controlled, pressure drop may be avoided and inefficiencies may not creep in. 5. What is the best way to maintain pneumatic angle seat valves? Regularly inspect and clean the valve, check for air leaks, replace worn components, and ensure proper lubrication.
READ FULLHVAC systems are found in large buildings and play a vital role in making the interior environment comfortable, and safe. These systems are used in commercial as well as residential complexes to maintain climate control and air quality. A core component of HVAC systems is the steam solenoid valve which performs the function of control and efficiency. Solenoid valves distribute the steam flow in the system and also increase the energy efficiency and reliability of HVAC operation. In this blog we will discuss thorougly the applications, benefits and slecelcion choices of steam solenoid valves and how significant they are in the operation of an HVAC system. What Are Steam Solenoid Valves? Steam solenoid valves' main function is to regulate the steam flow in an HVAC system. This is done through the valve opening and closing periodically by the action of an electromagnetic force to speed up or reduce steam flow as required. How They Function? The essential element that drives the movement of the steam solenoid valve is the electromagnetic coil. Once the coil is in an energized state it emits a magnetic field which moves the plunger. The movement of the injector opens or closes the valve. The whole process happens fast and without delay which means that real-time adjustments are possible. Types of Steam Solenoid Valves in HVAC Normally Closed (NC): Valve is closed when de-energized and opens only when power flows. These type of valves are used as safety mechanisms when steam flow needs to stop during power failures. Normally Open (NO): Normally seen in systems that deliver continuous flow, this valve stays open in a de-energized state and closes once energized. Two-way valves regulate steam flow within a single line. Three-way valves: can switch flow between multiple lines, which is ideal for complex system design. Multiple types of solenoid valves mean that they can fulfill unique HVAC requirements easily. Importance of Steam Solenoid Valves in HVAC Systems Steam solenoid valves are considered vital as they help to smoothly control the HVAC systems. Control of steal flow tends to have a direct impact on energy consumption and efficiency within the system on question. Main Functions: Energy Efficiency Through steam regulation the solenoid valves minimize energy wastage thus boosting the energy usage of the HVAC system and reducing the operational expense as well. System Precision These valves ensure climate control through keeping a tight control on temperature and humidity levels. Automation HVAC systems are dependent on automation and with steam solenoid valve this is made effortless as they make it possible for real-time adjustments and intelligent controls. In the absence of these valves HVAC systems would be unable to deliver an operational performance that meets the standartds of efficiency and reliability. Applications in Heating Systems In heating applications steam flow regulation is vital for effective functioning and steam solenoid valves are core component of such applications. Radiators: solenoid valves ensure steady steam flow to deliver uniform heating. Heat exchangers: Control heat transfer in systems that operate on the principle of steam-to-liquid exchange. Underfloor Heating Systems: Evenly distribute steam across the floor for uniform heating. Steam solenoid valves are quite versatile and can be used in all kinds of heating solutions whether residential, commercial or industrial. Applications in Ventilation Systems The purpose of ventilation system is to maintain ideal humidity level for making the environment comfortable, healthy and efficient. This is done through controlled steam flow delivery to humidifiers and ventilation ducts. Solenoid valves are thus vital for maintaining the steam flow. Benefits of Ventilation Health and Comfort: An adequate humidity level reduces respiratory illnesses and also creates a comfortable atmosphere Controlled environments: Data centers and hospitals need a controlled environment and solenoid valves help maintain constant temperature of the environement. Since solenoid valves are a core component of ventilation systems, they solve a wide range of human needs. Applications in Air Conditioning Systems Although steam is generally utilized for heating, it has its function in air conditioning system. Steam solenoid valves also control heat flow for cooling which raises operational efficiency and reliability. Advantages in Air Conditioning Energy Efficiency: Better control of steam flow reduces energy wastage in a cooling cycle. System Durability: Streamline steam regulation contributes to a longer system usage life as it reduces wear resistance on cooling components. So, you can see for yourself that the diverse applications of solenoid valves are vital for controlling temperature. Advantages of Using Steam Solenoid Valves in HVAC HVAC system performance gets a lot of boost if steam solenoid valves are fitted. Let us see exactly how these valves enhance performance of the system. Energy Efficiency: Solenoid valves make it possible to accurately control steam usage which drastically reduces energy wastage making the system energy efficient and eco-friendly. Durability: Solenoid valves have a robust build and tolerate high temeperatures and pressures and so they do not get damaged easily and this contributes to system longevity. Automation Integration: These valves can be connected with monitoring systems which means that the HVAC system can be controlled easily. Cost Efficiency: Solenoid valves make the system efficient, and this helps in reducing maintenance expenses as well. Considerations When Selecting Steam Solenoid Valves To ensure that an HVAC system delivers peak performance, the selection of the right steam solenoid valve is crucial. Following are factors that you need to keep in mind for making the correct choice Material Compatibility: Valve materials should be compatible with steam and constructed to be invulnerable to rust and corrosion. Operating Pressure and Temperature: System operational conditions should be matched with the specification of the solenoid valve Valve Size and Configuration: The sizing of the valve shold be adequate enough for uninterrupted and uniform steam flow. By carefully taking into account these attributes, you can make the right selection and purchase solenoid valves that maximize performance. Emerging trends in Steam Solenoid Valves Smart Technology: Latest valves come fitted with sensors and IoT technologies that enhance their connectivity allowing for real-time monitoring. Sustainable Materials: With an increased focus on climate awareness, latest solenoid valve models are made from eco-friendly materials to reduce the environmental burden Role of Suppliers in Quality HVAC Systems It is important to select a good supplier in order to have high-quality components and system performance. Reliable suppliers provide: Durable Products: Special types of valves for difficult operating conditions. Expert Advice: Assistance in selecting of the right valves suitable for certain HVAC environments. Long-term Support: Offering potential for high reliability, it is a fact that stock of spare parts provides genuine assurance. Partnering with trusted suppliers is the only way to create HVAC systems that are leading in efficiency and reliability. Conclusion The solenoid valves are the steam unsung heroes of an HVAC system. They serve an important role in controlling steam flow and energy efficiency within systems. It ranges from heating, ventilation, and air conditioning applications and depicts how useful these elements are. As the HVAC industry continues to advance, high-quality smart steam solenoid valves will be essential to stay ahead in energy-efficient solutions. Such investments enhance higher performance levels and sustainable dimension in business and homeowner HVAC applications. FAQs 1. What is the purpose of a steam solenoid valve in an HVAC system? Steam solenoid valves control the flow of steam within HVAC systems, ensuring precise regulation for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning applications. 2. Can steam solenoid valves be used in both residential and industrial HVAC setups? Yes, there steam solenoid valve is thus flexible and it can be applied in residential and or industrial HVAC system. 3. What components should be considered when selecting a steam solenoid valve? Key factors include the steam's pressure and temperature, the valve's material compatibility, size, and power requirements. 4. How do steam solenoid valves contribute to energy efficiency in HVAC systems? They conserve energy because they closely regulate the flow of steam, minimize on wastage and guarantee efficiency. 5. Are steam solenoid valves compatible with smart HVAC systems? Yes, modern steam solenoid valves can be integrated with smart HVAC systems for enhanced control and automation.
READ FULLIn the intricate world of industrial engineering, precision plays an enormous role. Among many sophisticated systems, one rather unassuming part happens to form its nucleus: the solenoid valve. Electromechanical valves are unsung heroes in regulating fluids and gases, enabling precise flow handling in various applications in divergent industrial segments. A solenoid valve is an engineering marvel that converts electrical signals into mechanical motions to control the flow of liquids or gases. Unlike generic stock items, a custom-engineered solenoid valve can offer specificity for substantially improving system performance, efficiency, and reliability. A custom solenoid valve is more than a simple piece of hardware; it's a custom solution for the particular demands of given operational environments. Whether for a high-pressure industrial process, advanced medical equipment development, or sophisticated automotive systems, the right custom solenoid valve can make a great difference. What are custom solenoid valves? At its core, a custom solenoid valve is an electromagnetic valve designed to meet specific operation conditions. While standard solenoid valves offer generic solutions, their custom variants allow for extensive customization across multiple parameters and thus provide targeted performance. Customizable features include the following: Materials: Brass for general industrial purposes Stainless steel for corrosive or high-temperature environments Advanced polymers provide lightweight, chemical-resistant solutions. Specifications: The size can vary between miniature to large industrial configurations. It ranges from low-pressure pneumatic operating pressure to high-pressure hydraulic loads. Voltage and current rates and response instances are assembled for specialized electrical specifications. The fact that these parameters may be unique means that there is scope for engineers to design valves that are perfectly 'tuned' to the system requirement they are being incorporated into – with the result that the compromises that are cost-effective standard solutions do not have to be made. Top Applications of Custom Solenoid Valves Across Industries Industrial Automation Custom-made solenoid valves enhance manufacturing precision by providing the proper control to pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Whether robotic, assembly-line automated systems or complex material-handling equipment, the valves ensure that they flow smoothly and operations remain hassle-free. Medical Equipment Precision is a matter of life and death in critical healthcare applications. Custom solenoid valves have crucial roles in oxygen delivery systems, diagnostic machines, and medical instrumentation, where exact flow control can impact patient outcomes. Automotive Industry Modern vehicles' fuel systems, engine controls, transmission, and emission controls use high-level solenoid valves. Custom-designed models assist automobile engineers in maximizing performance and fuel economy and meeting strict environmental guidelines. Oil and Gas Extreme environments call for extraordinary solutions. High-pressure, corrosive-resistant, specially designed solenoid valves manage complex fluid control processes in exploration, refining, and distribution infrastructure. Food and Beverage Specialized fluid control maintains hygienic standards, while custom solenoid valves guarantee quality and safety in products made with food-grade materials and precision in sanitary design. HVAC Systems Temperature and pressure control in HVAC systems rely on reliable and accurate valve operation. Specialized design of solenoid valves enables energy-efficient and responsive climate control solutions. Advantages of Custom Solenoid Valves The advantages of a custom solenoid valve are far beyond the basic functionality: Precision Engineering: Exactly matched to each operational requirement Improved Performance: Optimized for specific environmental and mechanical constraints Increased Longevity: Designed to Withstand Unique Stress Factors Cost-Effectiveness: Lower maintenance and replacement costs because of focused design. Choosing the Right Manufacturer: The Chisin Valve Advantage Not all manufacturers are equal in production when it comes to custom solenoid valves. Special opportunity in Chisin Valve that makes it a solution provider for valves and packaging is the high level of expertise and innovation by the company in the valve industry. Experience and Reputation: Chisin Valve's Proven Track Record 25+ years of industry-leading experience Trusted by Fortune 500 companies across multiple sectors Consistent track record of technological innovation Recognized leader in custom solenoid valve engineering Certifications: Chisin Valve's Commitment to Quality Comprehensive Certification Portfolio: SO 9001:2015 certified CE Mark compliant Industry-specific certifications include: API Standards ASME Quality Certifications International Manufacturing Standards Unmatched Customization Range Chisin Valve Customization Capabilities: Tailored solutions for unique industrial requirements Comprehensive engineering support End-to-end custom valve design and manufacturing Extensive portfolio of successful custom projects Evaluation Steps: Why Chisin Valve Stands Apart Comprehensive Portfolio Review Detailed case studies available Transparent project documentation Extensive range of successful implementations across industries Demonstrable expertise in complex valve engineering Customer-Centric Approach Robust testimonial program Performance feedback mechanisms Long-term client relationships Continuous improvement based on customer insights Prototype and Testing Excellence Advanced prototype development Real-world performance evaluation Rigorous quality assurance processes Free consultation and initial prototype assessment Critical Questions Answered by Chisin Valve Lead Times Fastest turnaround in the industry Typical project completion: 4-6 weeks Expedited options available for urgent requirements Transparent project timeline communication After-Sales Support Comprehensive 24/7 technical support 2-year warranty on all custom valve solutions Dedicated customer success managers Free consultation and maintenance guidance Future Scalability Adaptive manufacturing capabilities Flexible production infrastructure Investment in continuous technological upgrades Capacity to handle growing and complex project requirements Why Choose Chisin Valve? Unique Value Propositions: Cutting-edge engineering expertise Proven reliability across industries Commitment to technological innovation Personalized customer solutions Competitive Pricing Global manufacturing standards Conclusion Chisin Valve is more than a valve manufacturer—we are your strategic partner in achieving unprecedented fluid and gas control performance. Our custom solenoid valves are engineered to transform your operational capabilities. Frequently Asked Questions Q1: How long does a custom-designed solenoid valve typically last? In its ideal design and implementation, a custom solenoid valve can last 5 to 10 years, depending on the adopted application and setting. Q2: Is a customized solenoid valve costlier? As their name suggests, they are usually higher in price at their conception or initial stage. Yet, almost always, long-term savings compensate for the investment with better efficiency and drastically reducing maintenance. Q3: How soon can custom-made solenoid valves be manufactured? Depending on complexity and manufacturer capabilities, typical lead times range from 4-12 weeks.
READ FULL